For thousands of years, the Yellow River has nurtured the splendid Chinese civilization. The Dahaihe River is located in the northwest of China’s Loess Plateau. It is the largest tributary of the Yellow River water system flowing through the Hetao Plain. It is the “mother river” of Hohhot , Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Additionally, it is located in the East Asia-Australasia international migration line, and is an important biological migration corridor and water sponge corridor.
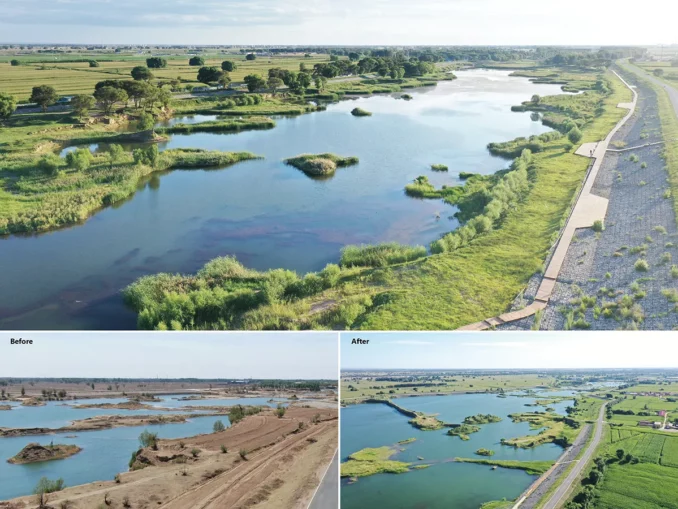
However, the Daheihe River faced some serious ecological challenges, including illegal sand mining, deterioration of the water system, soil desertification, and habitat degradation.
Daheihe Country Park is a typical demonstration section of river ecological management. The design focuses on four aspects: biodiversity conservation, sponge ecology construction, enhancement of recreational functions, and integration of rural culture and tourism. A 490-hectare open reserve is established along the 12.9-kilometer Daheihe River.

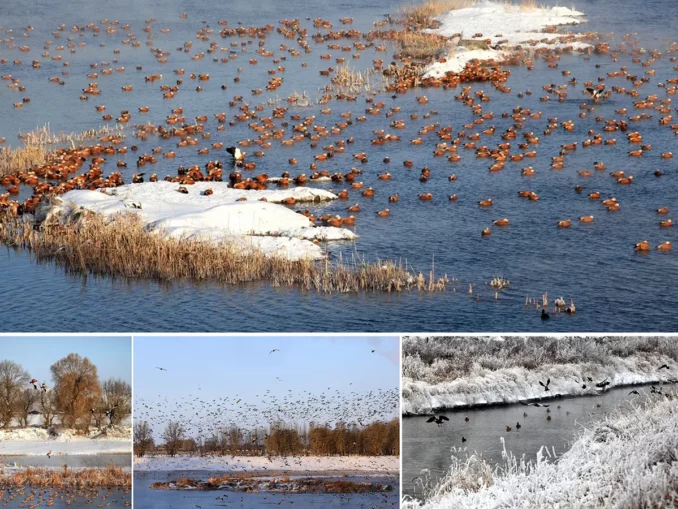
One year after its construction, thousands of Class II national protected animals – shelduck came here to roost. Many kinds of birds live together here, which fully shows that the Dahaihe River has successfully transformed from a polluted and damaged river into a highly adaptive ecosystem, providing a model for ecological restoration in the arid areas of the northwest.
Site Analysis & Challenges
Paradise for Migratory Birds is located in Hohhot, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, with a total length of 12.9 kilometers. The present situation is characterized by large trees, rich landforms and diverse land use types. However, the disorderly sand mining activities have increasingly eroded ecological resources such as water systems, wetlands and forestlands. It due to serious soil erosion, soil desertification, destruction of biological habitat and lack of cultural and tourism resources.

Design Strategy
With the improvement of natural habitat as the core, a series of measures such as river dredging, water body restoration, vegetation restoration and insect hotel are implemented to achieve biodiversity protection. The enrichment of waterfront vegetation community can be achieved by dredging the main river, purifying the water quality of the guest water, repairing the bare sand soil, shaping the wetland beach and ecological revetment.
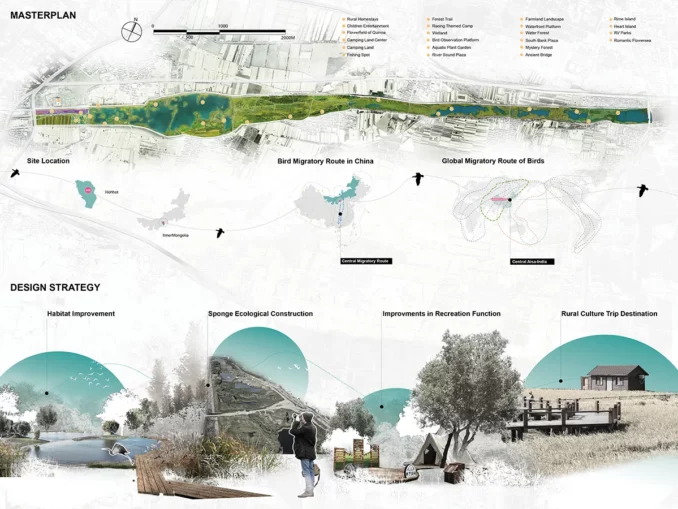
Multiple sponge facilities such as ecological grass ditch and rainwater purification wetland are designed for different land types to collect, filter and purify the imported water and improve the ecological service function of the riverbank.
Within the limits of recreational capacity and ecological capacity, low-disturbance recreational activities are placed to form diversified recreational nodes such as under forest camping, RV camp, bird watching platform, etc., which enriching the ecological themed recreational system and natural education system.
In terms of the integration of rural culture and tourism, based on the status quo of the village and ecological opportunities, with “Zhaojun culture, parent-child holy land, and harmonious countryside” as the core, it is committed to creating a tourism resort in Zhaojun Water town that integrates “parent-child tide play experience, harmonious countryside construction, and Zhaojun culture and art”, promoting the integrated development of agricultural culture and tourism, and realizing the ecological sharing of people, birds and cities.
Spatial Nodes Design
Planning layout:
According to the complex land properties, the design effectively respects the natural landform, and forms the overall structure of “one belt, three sections and ten views”. It builds a comprehensive value system for the integration of natural ecology, recreation, leisure and cultural tourism for Daheihe River.
01 Shaping a Resilient Eco-Sponge Belt along the Daheihe River
Daheihe River Ecological Sponge has three major design features, the first is to prioritize the protection of permanent basic farmland and high-quality farmland around the city.
The second is habitat improvement along the route, the design follows the principle of low-impact development, and the 13km main river is dredged to control water pollution with ecological methods. At the same time, biodiversity conservation is achieved through vegetation restoration and insect hotel construction.
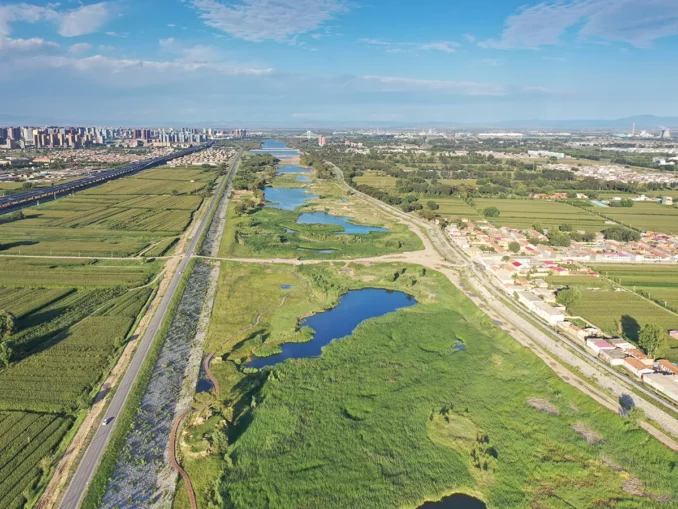

Finally, the construction of sponge corridors is also crucial, the Daheihe River is an important area for ecological protection in the Yellow River basin, an important river ecological corridor in the city and an important sponge corridor for imported water in the built-up area. Design through the construction of a once-in-a-hundred years flood embankment and dredging the main river to achieve smooth flow of water. Based on the principle of receiving all the imported water, measures such as ecological planting ditch, ecological parking lot, farmland wetland, vegetation buffer zone and rainwater purification wetland are selected for the multi-type land such as water area, inland beach, cultivated land and forest land, and finally discharged into the Daheihe River through multiple buffering. A series of filtration measures can supplement groundwater, regulate runoff, detain flood and reduce runoff pollutants, achieve the target of 90% annual runoff control rate, and create a river landscape with flood control, ecological and recreational functions.
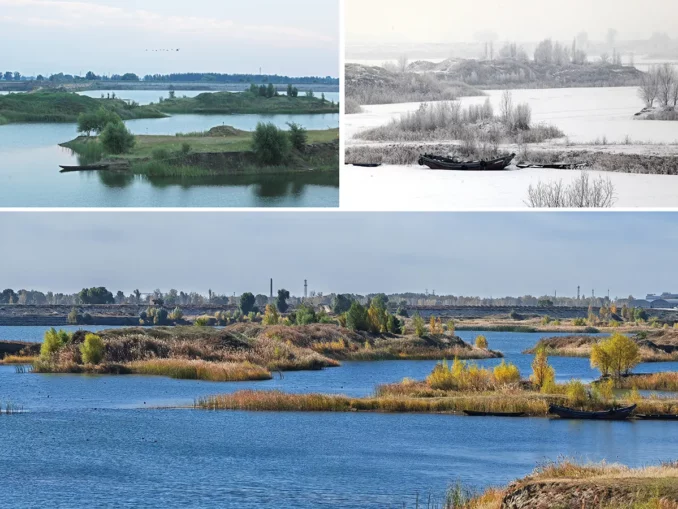

02 Creating a Biodiverse Habitat
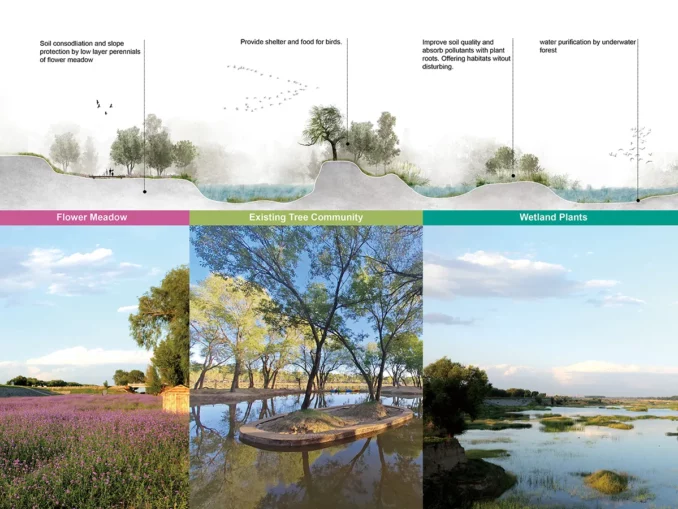
The section of“Wetland” takes the ecological restoration of the beach as the core, and preserves the current topography and various types of vegetation to the maximum extent. In the exposed area of loess, local suitable vegetation such as awnless brome and stiflgrass is scattered to achieve green cover. After three years, the green return situation is good.
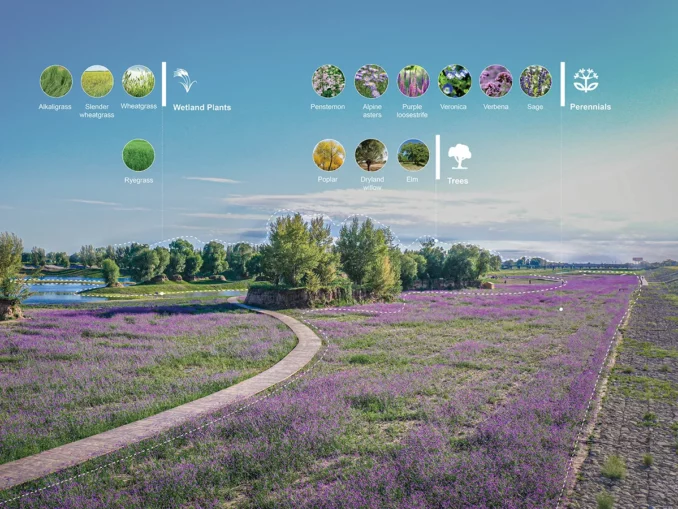
The core of the “Thousand Islets Lake” is the ecological restoration of 204 hectares of water. Combined with the current water depth, the design mainly selects the dwarf bittergrass as the main group species, which has the characteristics of low light resistance, pollution resistance, high temperature resistance, salt resistance, etc., combined with the impact resistance and water resistance varieties such as bittergrass and ricodendron, to form a low plant underwater forest. In particular, it is worth mentioning the restoration of ecological stepping stones such as isolated islands in the water to form safe and undisturbed breeding grounds, providing quality living space for birds, fish and amphibians.
At the same time, rainwater purification wetland was designed for the drainage outlet to achieve water purification. One year after its construction, thousands of national Class II protected animals – shelduck flocks came here to feed and roost. Groups of black storks, mallard ducks, egrets, coot chickens and herons symbiosis here, reflecting remarkable ecological restoration results.
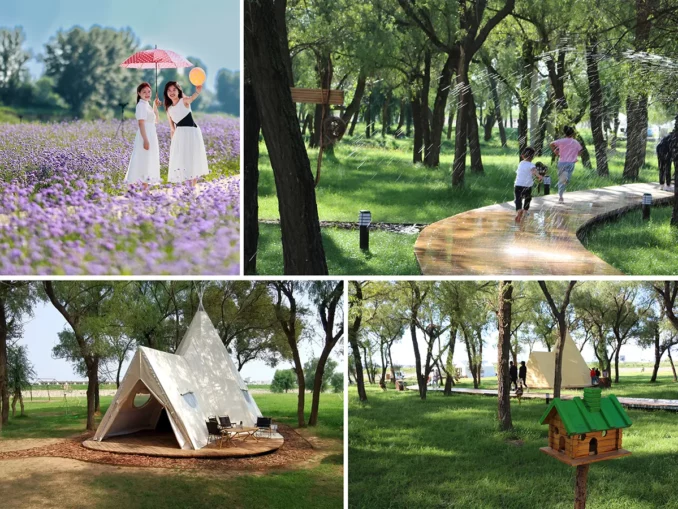
03 Integrate rural revitalization and recreation into multiple tour nodes
Combined with the characteristics of the current trees, the waterfront walking path and camping operation are placed to further expand the under-forest recreation space and create a diversified recreation destination. With the overall goal of “Zhaojun Water Town Tourism Resort” as the cultural tourism, there are ten main landscape nodes along the route, including three cultural landscapes and seven natural landscapes. At the same time, the effective collection and recycling of sewage and garbage in villages will be realized, and the development of waste-free villages and pollution-free agriculture will be promoted.

Social Significance
The design and construction of the project promoted the promulgation of the “Regulations on Ecological Protection of Daheihe Country Park in Hohhot”, passed the ecological legislation of the National People’s Congress, effectively protected the ecological space of the riverbank in the long term, and reasonably restricted the development behavior and operation content. After the construction of the project, the local government and citizens’ recognition of the ecological restoration of the Dahei River was greatly improved.
The project provides clear implementation path guidance for improving biodiversity and habitats in the arid grassland cities of Northwest China. It gradually restores water ecological corridors, builds near-natural vegetation systems, and promotes the sustainable development of biodiversity.

Combined with the trend of suburban recreation and eco-tourism in recent years, the design provides urban residents with better countryside sightseeing destinations, improves the infrastructure of surrounding villages, promotes the renewal of business patterns of surrounding villages, promotes the development of tourism-related tertiary industry, provides the direction for the upgrading of agricultural industry, and brings more employment opportunities for villagers. The ecological value is transformed into social value and economic value.
Paradise for Migratory Birds | Ecological Restoration of Daheihe River in Inner Mongolia, China
Design company: Shanghai Landscape Architecture Garden Design & Research Institute Co., Ltd (SLADI)
Design chief: Zhaoxia Zhang, Yan Li
Design team: Hong Jiang, Mingxi Gao, Yueyue Fan, Wenting Ji, Peng Yu, Chengyu Qian, Hanchuan Liu, Xiaolan Wu, Chong Li, Xiaojun Wang, Xinying He, Xuechao Huang, Baojuan Wang, Yu Shi, Chenghui Zhao, Boyang Xia, Shupeng Lin, Yu Ding, Guibing Bian
Project location: The Inner Mongolia City of Hohhot
Client: Hohhot housing and Urban-Rural development Bureau
Photography Credit: Le Yan
Landscape construction company: Mengcao Ecological Environment (Group) Co., LTD.
→ Continue reading at World Landscape Architecture
